Introduction
IIn the ever-evolving landscape of customer relationship management (CRM), Salesforce stands out as a trailblazer. One of the key features that contribute to its robustness is the use of audit fields. These fields play a pivotal role in maintaining data integrity and providing a transparent trail of changes within the Salesforce ecosystem. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of audit fields, exploring what they are, why they are non-editable, and their crucial role in ensuring data accuracy and security.
What are Audit Fields?
Audit fields in Salesforce are special fields designed to track and record crucial information about a record's lifecycle. They capture metadata about when a record was created, last modified, and who performed these actions. The three main audit fields in Salesforce are:
- Created By: This field records the user who initially created the record.
- Created Date: It stores the timestamp of when the record was first created.
- Last Modified By: This field captures the user who last modified the record.
- Last Modified Date: It holds the timestamp of the last modification made to the record.
Enable the 'Create Audit Fields' permission
- From Setup, enter User in Quick Find box and select User Interface.
- Select the checkbox for Enable "Set Audit Fields upon Record Creation" and "Update Records with Inactive Owners" User Permissions.
- Click Save.
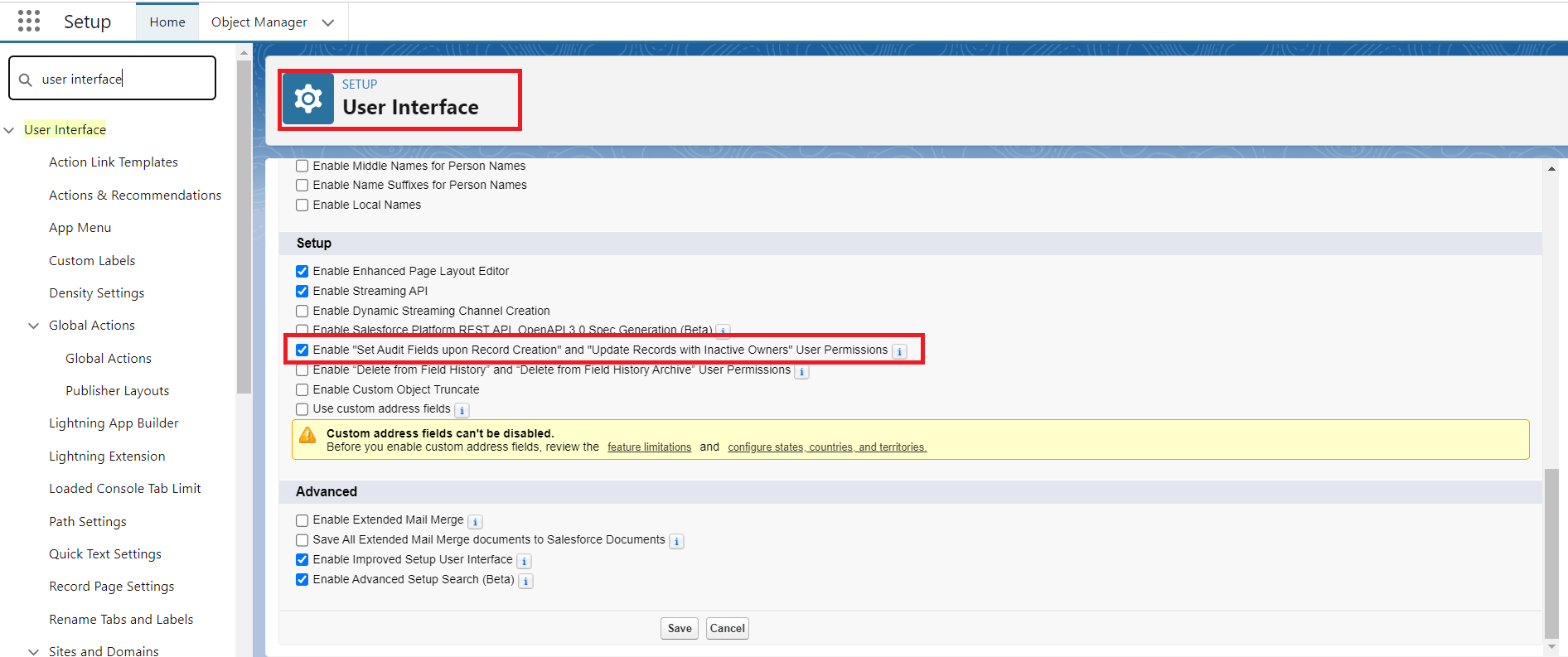
Figure 1: Enable the 'Create Audit Fields' permission.
Enable the permission 'Create Audit Fields' for standard profiles
Create a Permission Set
- Go to Salesforce Classic: Setup | Manage Users | Permission Sets Lightning Experience: Gear icon | Setup | Users | Permission Sets
- Click New.
- Enter Permission Set information such as 'Label' and 'Description'.
- Optionally, specify a 'User license' to restrict this Permission Set to Users with specific licenses.
- Click Save.
- On the next page, Go to System Permissions.
- Click Edit.
- Find 'Set Audit Fields upon Record Creation' and check the box for it. Note: If you do not see this option it's likely that 'Set Audit Fields upon Record Creation' and 'Update Records with Inactive Owners' is not currently enabled.
- Click Save.
Assign the Permission Set
- Go to: Salesforce Classic: Setup | Manage Users | Permission Sets Lightning Experience: Gear icon | Setup | Users | Permission Sets
- Select the Permission Set for the 'Audit Fields.'
- Click Manage Assignments.
- Click Add Assignments.
- Select the User to whom you want to assign the 'Permission Set.'
- Click Assign.
- Click Done.
Why are Audit Fields Non-Editable?
One of the distinctive characteristics of audit fields is their non-editable nature. This intentional design choice is rooted in the principle of data integrity and accountability. By preventing users from altering these fields, Salesforce ensures the reliability of the recorded information. Non-editable audit fields serve as immutable markers, preserving the historical context of each record.
Allowing modification of these fields would compromise the accuracy and trustworthiness of the audit trail. If users could manipulate the creation or modification details, it would undermine the credibility of the recorded information and hinder the ability to trace changes accurately.
The Purpose of Audit Fields in Salesforce:
- Historical Tracking: Audit fields provide a historical timeline of a record's journey within Salesforce. This is vital for compliance, auditing, and maintaining a comprehensive record of data changes over time.
- User Accountability: The non-editable nature of audit fields ensures that the information they contain is reliable and reflects the actual actions of users. This accountability is crucial for maintaining a transparent and trustworthy CRM environment.
- Security and Compliance: In industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as healthcare or finance, the ability to track changes to sensitive data is essential. Audit fields contribute to compliance efforts by offering an unalterable record of data modifications.
- Troubleshooting and Debugging: When issues arise, having a detailed audit trail can significantly simplify the troubleshooting process. Administrators can review the audit fields to identify when and by whom a specific change occurred.
- User Adoption and Training: The visibility provided by audit fields can also support user adoption and training efforts. Users can understand how their actions impact records and learn from the historical data captured in these fields.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, audit fields in Salesforce serve as guardians of data integrity, ensuring a reliable and transparent record of changes. Their non-editable nature is a deliberate choice to maintain the credibility of the audit trail. As organizations continue to prioritize data accuracy, security, and compliance, the role of audit fields in Salesforce becomes increasingly significant. Embracing these features can unlock a wealth of benefits, from regulatory compliance to enhanced user accountability and streamlined troubleshooting processes.
For any queries please reach out to support@astreait.com